
In view of the lack of information about review processes and study validity, and failure to report measures of statistical variability, the authors’ conclusions should be interpreted with caution. The choice of a narrative synthesis to combine the studies was appropriate, given their heterogeneity, but clinical significance of the findings was difficult to evaluate due to the lack of focus on a primary outcome and failure to report any measures of statistical variability. Treatment: Buckle fractures are stable fractures that can usually be treated with a cast or removable splint for 3-4 weeks to protect and support the injured area while it heals. If an operation is needed, we will talk to you about this in.
Will my child need an operation No, not usually. Results In terms of diagnosis, the ultrasound was found to be more sensitive than X-rays for diagnosing these fractures. Patients were randomized (single blindly) to the studied treatment groups.
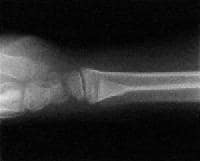
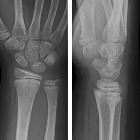
These factors made it difficult to assess the reliability of the evidence presented. Application of Removable Wrist Splint in the Management of Distal Fore- arm Torus Fractures 2013 Saeed Safari Background: There is considerable variation in the treatment of distal forearm torus fractures (DFTF), from soft bandaging to cast immobilization. The diagnosis, assessment, fracture reduction, and casting of distal forearm fractures in children and the care of pediatric proximal or midshaft forearm fractures are discussed separately: (See 'Distal forearm fractures in children: Diagnosis and assessment'. Buckle fractures usually heal in 3 to 4 weeks. Methods We prospectively included 79 patients suffering from undisplaced greenstick and torus fractures of the distal radius. Traditional approaches to their management involved immobilisation in a circumferential cast but the evidence now supports the use of removable splints with or without radiological and clinical follow-up. No information about study validity or funding was reported. Torus fractures, also known as buckle fractures, of the distal radius are a very common reason for presentation to emergency departments. It was unclear whether steps were taken to minimise risk of reviewer bias and error by having more than one reviewer select studies and extract data. The apparent restrictions to published English-language studies meant that the review was prone to publication and language biases. A greenstick fracture is a partial thickness fracture where only the cortex and periosteum are interrupted on one side of the bone while they remain uninterrupted on the other side.
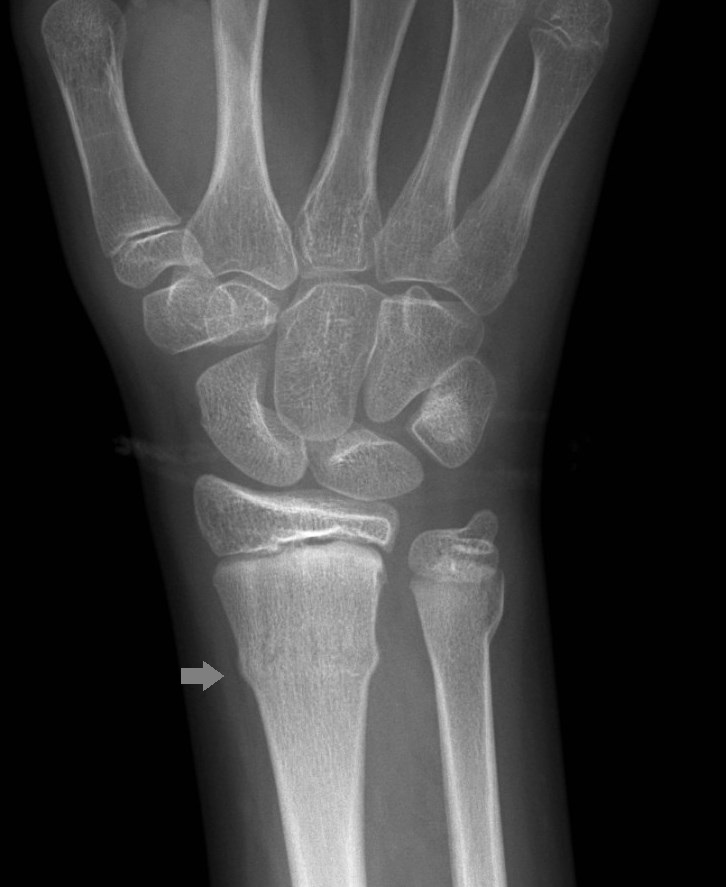
Relevant sources were searched for studies. These fracture patterns include greenstick, torus, and spiral injuries, which are bending injuries rather than full-thickness cortical breaks. The objectives and inclusion criteria of the review were clear.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
